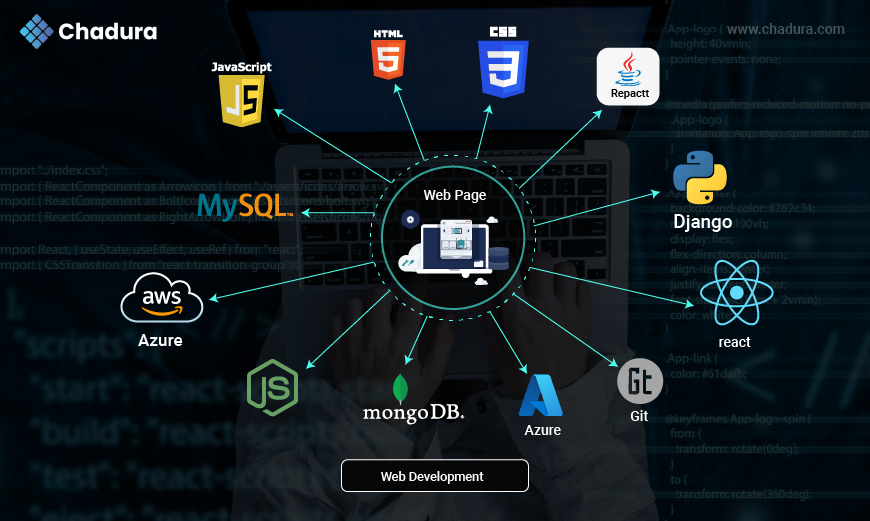
Web development is the process of creating websites and web applications. Web development refers to building, creating, and maintaining websites. It includes aspects such as web design, web publishing, web programming, and database management. It is the creation of an application that works over the internet
It includes:
- Frontend development (client-side) – focuses on what users see and interact with.
- Backend development (server-side) – manages databases, server logic, and API interactions.
- Full-stack development – combines frontend and backend skills.
Frontend Technologies (Client-Side)
Frontend technologies are used to build the visual and interactive part of a website that users see and interact with in their browsers. In this module, we explore the core technologies that run in the user’s browser—the client side—including how web pages are structured, styled, and made interactive, building everything users see and interact with.
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is the language used to create the basic structure and content of web pages. It uses elements, tags, and attributes to organize text, images, and links.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is used to style the HTML content. It controls colors, fonts, layouts, and how the page looks on different devicesMore importantly, CSS enables you to do this independent of the HTML that makes up each web page.
- JS (JavaScript): JavaScript adds life to web pages by making them interactive. It handles things like buttons, animations, and form checks.
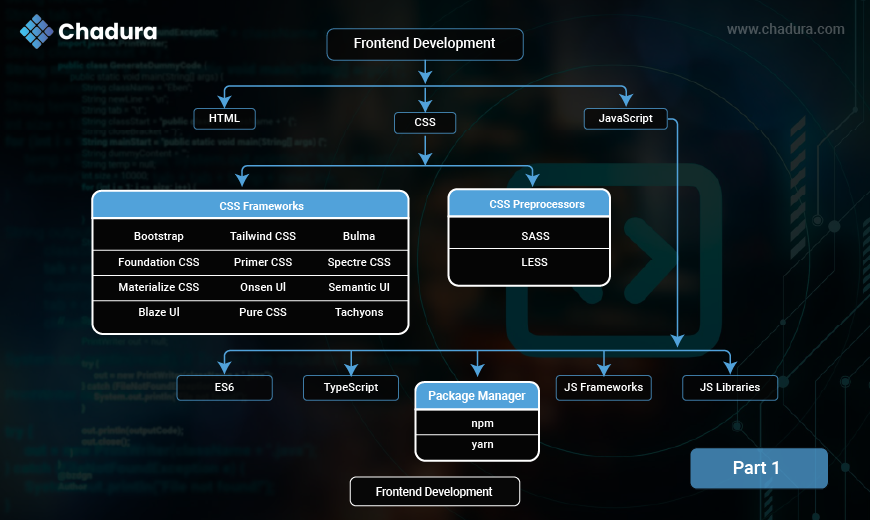
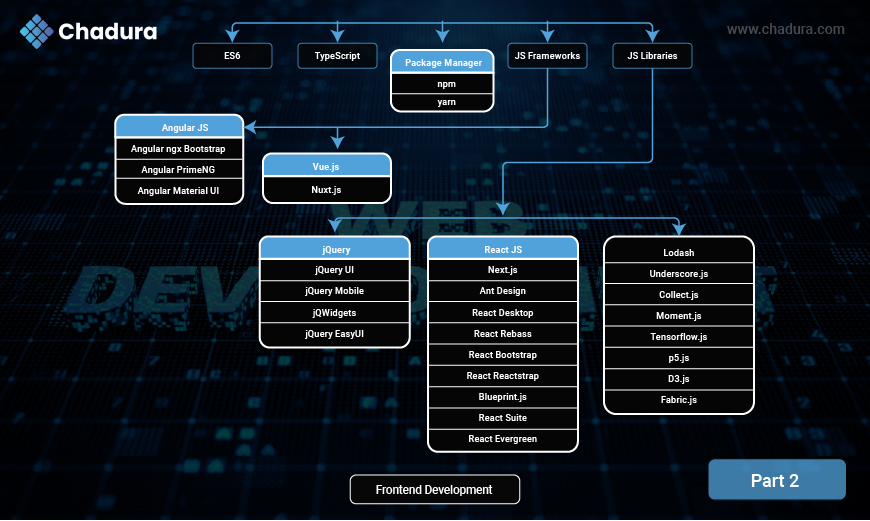
- ES6 (ECMAScript 6) : The 6th edition of JavaScript (2015) that introduced modern features like let/const, arrow functions, promises, classes, and modules — making JavaScript cleaner and more powerful.
- TypeScript : A superset of JavaScript that adds static typing, interfaces, and better tooling — helping developers catch bugs early and write more maintainable code.
- JavaScript Frameworks : Pre-built structures for building complex web apps faster.
Examples: React (library, often treated as a framework), Angular, Vue.js. - JavaScript Libraries :Reusable code collections for specific tasks, like DOM manipulation or UI components.
Examples: jQuery, Lodash, D3.js, Chart.js. - Package Manager : Tools that help install, update, and manage external libraries and dependencies in your project.
- npm (Node Package Manager): The default package manager for Node.js, widely used to install JavaScript libraries and tools.
- Yarn : An alternative package manager to npm, developed by Facebook, known for faster installs, offline support, and better dependency management.
- AngularJS : A structural JavaScript framework for building dynamic web apps. Uses HTML as the template language and extends it with directives.
- Vue.js : A progressive JavaScript framework used for building user interfaces. It's lightweight, flexible, and easy to integrate with other projects.
- jQuery : A fast, small JavaScript library that simplifies DOM manipulation, event handling, and Ajax calls with an easy-to-use syntax.
- ReactJS : A JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building interactive user interfaces. Uses a component-based architecture and a virtual DOM for fast rendering.
- Lodash : A utility library that provides helpful functions for manipulating arrays, objects, and other data types, making JavaScript easier to work with.
Key Features:
- Focus on user interface (UI) and user experience (UX)
- Ensure responsiveness and performance across devices
- Implement animations, navigation, and dynamic content
Popular Frontend Technologies:
- HTML5 – Structures content
- CSS3 – Styles and layouts
- JavaScript – Adds interactivity
- Frameworks: React, Vue.js, Angular, Svelte
- Styling Tools: Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap, Sass
Backend Technologies (Server-Side)
Backend technologies handle the behind-the-scenes logic that powers websites and apps, including databases, servers, and APIs.
PHP, Python, Ruby, Node.js, Java, C, and C++ are popular programming languages used for various development needs:
- PHP is mainly used for server-side web development.
- Python is known for its simplicity and is widely used in web, AI, and automation.
- Ruby emphasizes developer productivity, popular with web frameworks like Rails.
- Node.js runs JavaScript on the server, great for fast, scalable apps.
- Java is a robust, cross-platform language used in enterprise and Android development.
- C offers low-level programming for system software and embedded systems.
- C++ builds on C with object-oriented features for high-performance apps.
Framework: A framework is a pre-built set of tools and libraries that helps developers build applications faster and more efficiently.It provides a structured way to write code, handle common tasks like routing, database access, and user authentication, so developers don’t have to build everything from scratch.
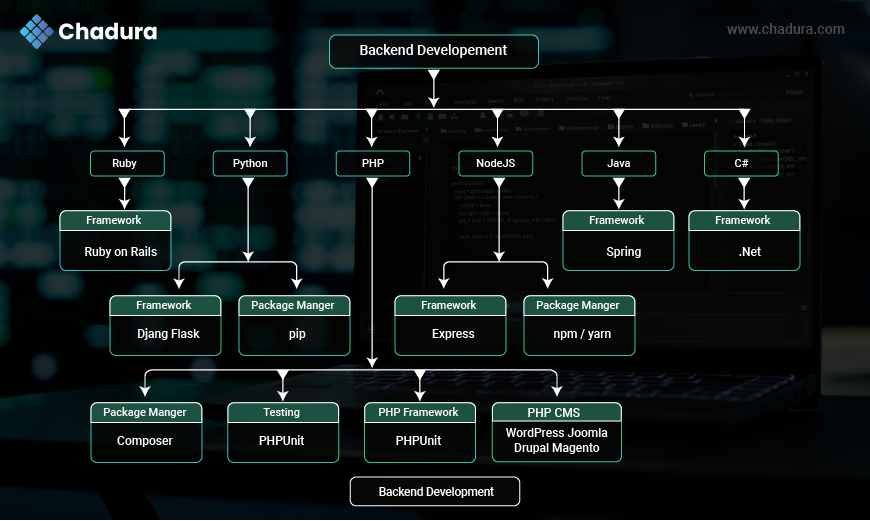
- PHP – Laravel : A modern PHP framework known for its elegant syntax, built-in tools, and MVC architecture. Ideal for web apps with routing, authentication, and templating.
- Python – Django / Flask : A high-level framework that promotes rapid development and clean design. Comes with admin panel, ORM, and security features.
- Flask: A lightweight, flexible microframework for building small to medium web apps.
- Ruby – Ruby on Rails : A full-stack web framework following “convention over configuration.” Great for quickly building database-backed web apps.
- Node.js – Express.js : A minimal and fast framework for building web applications and APIs using JavaScript on the server side.
- Java – Spring Boot : A powerful framework for creating enterprise-grade applications with minimal setup. Supports microservices, REST APIs, and security.
- C – N/A (Usually not framework-based) : C is low-level and procedural, typically not used with frameworks. It's more common in systems and embedded programming.
- C++ – Qt / Boost : Qt: A C++ framework for developing cross-platform GUI apps.
- Boost: A collection of libraries to support advanced C++ features like file systems, threading, and math operations.
Key Features:
- Manage data storage, authentication, and business logic
- Handle requests and responses between client and server
- Provide secure and scalable operations
Popular Backend Technologies:
Languages: Node.js (JavaScript), Python, PHP, Ruby, Go, Java, Rust
Frameworks: Express.js, Django, Laravel, Ruby on Rails
Databases: PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, Redis
APIs: REST, GraphQL, gRPC
Server-Side Programming Languages
In Backend Development, Server-side programming languages are used to write code that runs on the server, not in the user’s browser. This server-side scripting handles tasks like processing data, managing databases, and controlling how the website works behind the scenes
Below are some popular languages used to build the back end of web applications:
JavaScript/Node.js:JavaScript is a popular programming language mainly used to add interactivity on the client side (in browsers). With Node.js, JavaScript can also run on the server side. Node.js is an open-source environment that allows JavaScript to build fast, scalable back-end services like APIs. Many big companies like PayPal, Uber, and Netflix use Node.js for their server-side code.
- PHP: PHP is a server-side scripting language designed specifically for web development. Since PHP code executed on the server-side, so it is called a server-side scripting language.
- Python: Python is a programming language that lets you work quickly and integrate systems more efficiently.
- Ruby: An object-oriented programming language designed to be simple and natural to use. Ruby helps developers write clean and readable code.
- Java: Java is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages and platforms. It is highly scalable. Java components are easily available.
- Golang(Go): Golang is a procedural and statically typed programming language having the syntax similar to C programming language. Sometimes it is termed as Go Programming Language.
- C#: A modern, object-oriented language often used to build web applications on Microsoft platforms.
Databases
A database is where a website’s data like user's data, product's data are stored and organized. It is part of the backend (server side) that manages and keeps this information safe. Websites use databases to save and access information like user details, content, and transactions. Some databases organize data in tables (called relational databases, like MySQL), while others store data in flexible formats (called NoSQL databases, like MongoDB).
There are basically two types of databases:
1. SQL/Relational Database
A relational database stores data in tables, similar to a spreadsheet, where each table has rows and columns. The rows hold individual records, and the columns define the data attributes. Tables can be linked to each other through special keys, allowing related data to be connected.
MySQL: MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that uses SQL for managing structured data. It’s known for its reliability, ease of use, and performance, widely used in web applications.
Postgre SQL: PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source relational database that supports advanced SQL features and complex queries. It handles structured data, ensures ACID compliance, and is known for its reliability and extensibility.
MariaDB: MariaDB is an open-source relational database that evolved from MySQL, offering improved performance, security, and features. It supports SQL queries, ACID compliance, and is highly compatible with MySQL.
2. NoSQL Databases
A NoSQL database stores data in a flexible, non-tabular format, unlike traditional relational databases. Instead of using tables with rows and columns, NoSQL databases might use documents, key-value pairs, wide-columns, or graphs to store data. This allows them to handle large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently. They are designed to scale easily and manage big data applications.
Mongodb: MongoDB is a NoSQL database storing data in JSON-like documents. It handles unstructured data, supports powerful queries, and scales easily across servers, making it popular for flexible, scalable applications.
Cassandra: Apache Cassandra is an open-source NoSQL database that is used for handling big data. It has the capability to handle structure, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Redis: Redis is an in-memory NoSQL database known for its speed. It supports various data structures like strings, hashes, and lists, making it ideal for caching, real-time analytics, and messaging.
Note: We useDatabase management systems help keep the data safe, organized, and easy to use.
APIs and Data Exchange Formats
During Website development, different software components and web applications constantly need to communicate and share information. For instance, the frontend of your web application (running in the user's browser) needs to get data from the backend (running on a server), or your application might need to fetch information from a third-party service like a weather provider or a payment gateway. This communication is made possible through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and standardized Data Formats.
Data Exchange formate for API Communication: When applications communicate via APIs, they need a common, structured way to represent the data being exchanged. This is where data formats come in.
JSON: JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a format for structuring data.
XML: Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable.
Version Control and Deployment
Developing a web application involves more than just writing code. Two critical processes that ensure a smooth, organized, and reliable development workflow are Version Control and Deployment.
Version control helps manage the evolution of your codebase, especially when working in teams, while deployment is the process of making your web application accessible to the world. Modern development practices tightly integrate these two concepts, often through automation.
Graphics
Graphical elements are one of the key feature of any webpage. They can be used to convey important points better than text does and beautify the webpage.
Canvas: The HTML “canvas” element is used to draw graphics via JavaScript.
SVG: SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics. It basically defines vector-based graphics in XML format.
Key Features:
- Manage data storage, authentication, and business logic
- Handle requests and responses between client and server
- Provide secure and scalable operations
Popular Backend Technologies:
- Languages: Node.js (JavaScript), Python, PHP, Ruby, Go, Java, Rust
- Frameworks: Express.js, Django, Laravel, Ruby on Rails
- Databases: PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB, Redis
- APIs: REST, GraphQL, gRPC
After completion of front end and backend the basic working of a web browser and how it interacts with a web server to load a webpage. Here's a breakdown of the process:
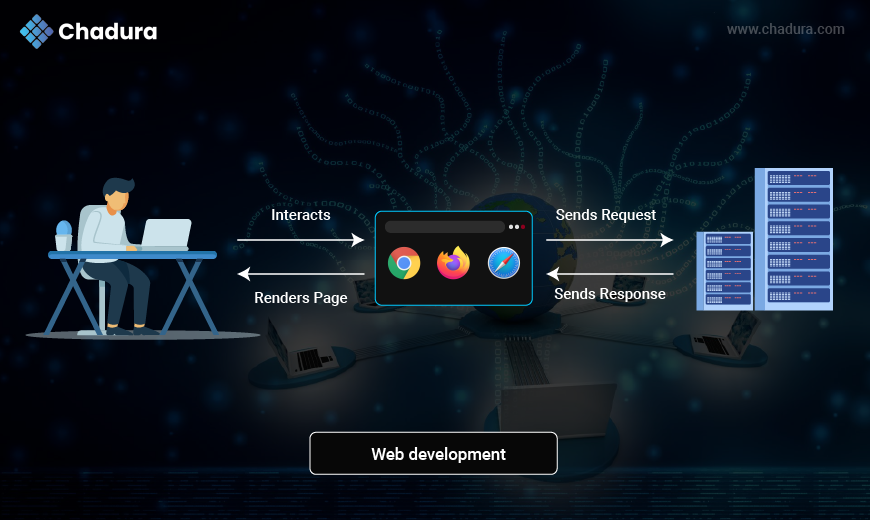
Step-by-Step Explanation:
User Interaction
- A person (the user) uses a computer and interacts with a web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari).
- This interaction could be entering a URL, clicking a link, submitting a form, etc.
Browser Sends Request
- The browser sends an HTTP request to the web server to fetch a webpage or resource (like HTML, CSS, images, etc.).
Server Sends Response
- The web server processes the request and sends back an HTTP response, which includes the requested data (typically a webpage).
Browser Renders Page
- The browser takes the response and renders the page, displaying the content to the user (text, images, forms, etc.).
User Continues Interacting
- The user can now view and interact with the page (click, scroll, type), and the cycle may repeat with more requests/responses.
Key Components in Image:
- User: Person using the web.
- Browser Icons: Chrome, Firefox, Safari – common web browsers.
- Server: Stores and delivers the requested content.