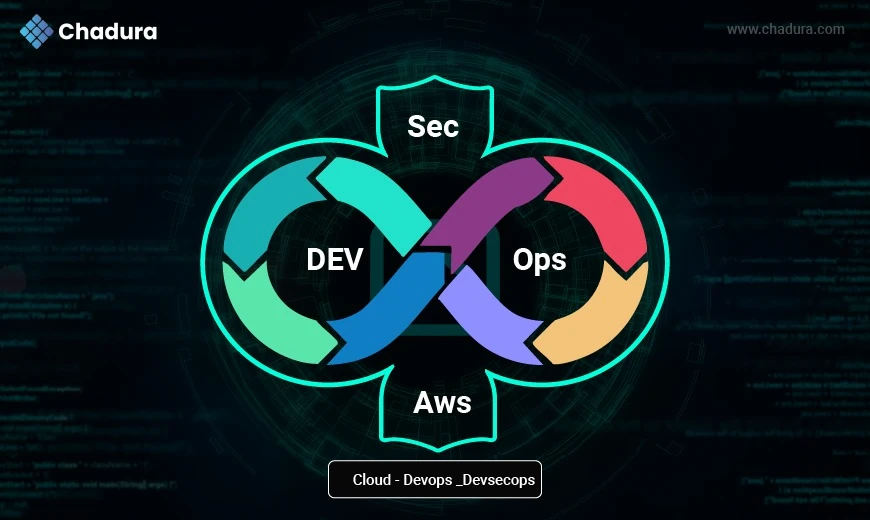
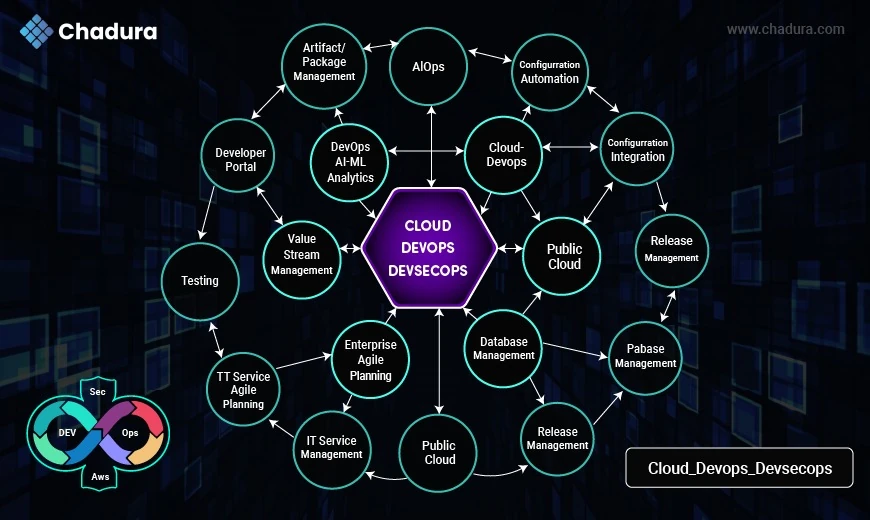
IT- Cloud - DevOps - DevsecOps
- AiOps
- Artifact/Package Management
- Collaboration
- Configuration Automation
- Container Orchestration
- Continuous Integration
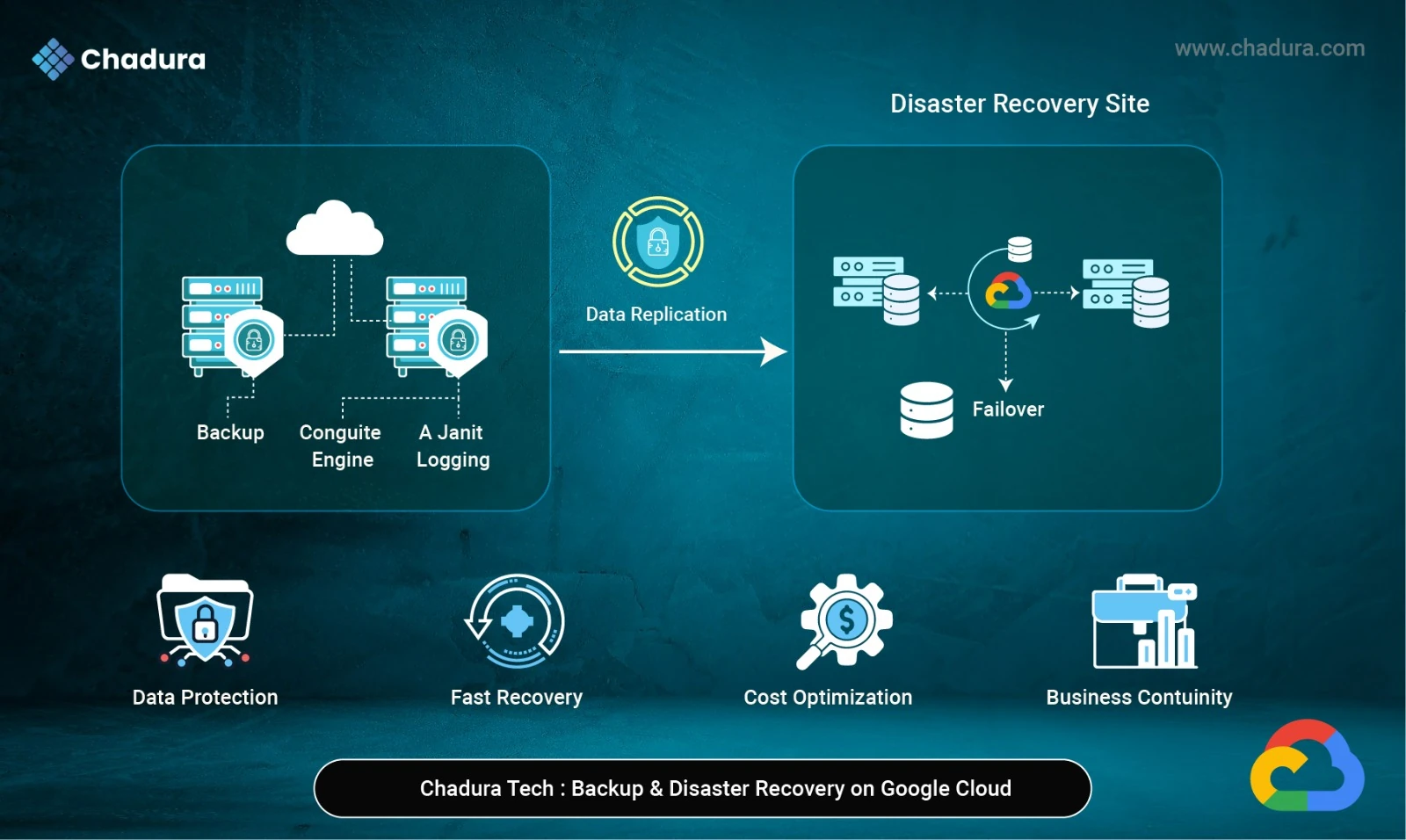
- Database Management
- Deployment
- Enterprise Agile Planning
- IT Service Management
- PaaS/Container Service
- Public Cloud
- Release Management
- Security
- Source Control Management
- Testing
- Value Stream Management
- Developer Portal
DevOps AI-ML Analytics
1.AiOps
AIOps is a term coined by Gartner that stands for Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations. It refers to the use of machine learning (ML) and big data analytics to enhance and automate IT operations processes such as:
- Monitoring
- Event correlation
- Anomaly detection
- Root cause analysis
- Incident response
- Capacity optimization
2. Artifact / Package Management
Artifact or Package Management is the process of storing, versioning, and distributing software components such as:
- Build artifacts (JARs, WARs, ZIPs)
- Code libraries (npm, pip, Ruby gems)
- Docker container images
- Infrastructure templates (e.g., Helm charts, Terraform modules)
It ensures that development, testing, and deployment environments always use trusted, reproducible, and versioned packages.
3. Collaboration
In DevOps, collaboration refers to the seamless communication, coordination, and teamwork between development, operations, security, QA, and other stakeholders throughout the software delivery lifecycle.
It enables faster releases, better problem-solving, and a shared ownership of success or failure — breaking down traditional silos between teams.
4. Configuration Automation
Configuration Automation refers to the process of automatically configuring servers, systems, applications, and infrastructure using code or templates — instead of doing it manually.
It is a key pillar of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and DevOps practices, enabling consistency, repeatability, and speed in IT environments.
5.Container Orchestration
Container orchestration is the automated management of containerized applications across clusters of machines. It handles:
- Deployment
- Scaling
- Networking
- Load balancing
- Resource allocation
- Failover and recovery
- Service discovery
6. Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) is a DevOps practice where developers frequently merge their code changes into a shared repository, and automated builds and tests are run immediately to validate the changes.
This helps catch bugs early, reduce integration problems, and enables faster, more reliable software delivery.
7. Database Management
Database Management refers to the processes, tools, and practices used to create, configure, maintain, monitor, secure, and optimize databases across development and production environments.
In a DevOps and cloud-native context, database management includes everything from schema migrations, automated backups, and monitoring, to performance tuning and infrastructure-as-code (IaC) provisioning.
8.Deployment
Deployment refers to the process of delivering software applications, services, or updates from a development or staging environment to a production environment where users can access them.
In DevOps, deployment is automated, reliable, and repeatable, and often integrated with CI/CD pipelines.
9.Enterprise Agile Planning
Enterprise Agile Planning (EAP) refers to the strategic planning, coordination, and governance of Agile software delivery across large teams, departments, or organizations. It ensures that Agile practices scale beyond individual teams to align with business goals, portfolios, and value streams.
It connects teams to strategy, enabling cross-functional collaboration, transparency, and faster delivery in enterprise environments.
10.IT Service Management
IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the strategic approach to designing, delivering, managing, and improving the way IT services are used within an organization.
Rather than just managing IT systems, ITSM focuses on delivering value to end-users and businesses through well-defined processes.
11.PaaS/Container Service
PaaS is a cloud computing model that provides a complete platform for developers to build, run, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. It includes operating systems, databases, middleware, runtime, and development tools.
Example: You write code → deploy it → platform takes care of everything else (OS, server, scaling, etc.)
12.Public Cloud
A public cloud is a cloud computing model where services such as storage, compute power, databases, and networking are provided by third-party vendors over the internet. These resources are shared among multiple tenants (organizations or individuals), making them cost-effective and scalable.
13.Release Management
Release Management is the process of planning, scheduling, coordinating, testing, and deploying software releases across development, staging, and production environments. It ensures that software is delivered reliably, efficiently, and with minimal risk.
14.Security
In the context of IT, Cloud, DevOps, and DevSecOps, security refers to the strategies, tools, and practices used to protect:
- Code
- Infrastructure
- Applications
- Data
Access rights
from unauthorized access, data breaches, vulnerabilities, and other threats throughout the software delivery lifecycle.
15.Source Control Management
Source Control Management (SCM) refers to the process and tools used to track changes in source code, collaborate across development teams, and manage multiple versions of code in software projects.
SCM is a foundational component of DevOps, Agile, and CI/CD practices.
13.Testing
Testing ensures that software behaves as expected, is secure, scalable, bug-free, and ready for production. In DevOps/DevSecOps, testing is not a separate phase but a continuous, automated, and integrated part of the development lifecycle.
It helps identify issues early, improves code quality, and ensures faster, safer releases.
14.Value Stream Management
Value Stream Management (VSM) is the practice of visualizing, tracking, and optimizing the flow of work (value) across the software delivery lifecycle — from idea to production. It enables organizations to maximize efficiency, remove bottlenecks, and deliver customer value faster.
In DevOps and IT, VSM connects strategy to execution by combining:
- Development
- Operations
- Security
- Business goals
14. Developer Portal
A Developer Portal is a centralized platform that provides developers with self-service access to tools, documentation, APIs, environments, and services they need to build, deploy, and manage software efficiently.
It accelerates development, promotes standardization, and ensures compliance and governance — all while reducing friction in the software delivery process.
15.DevOps AI-ML Analytics
DevOps AI/ML Analytics refers to the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques to enhance the automation, monitoring, decision-making, and efficiency of DevOps processes.
It's part of the broader field of AIOps — but specifically focused on development, delivery, deployment, and operations.
Flow Chart of Devsecops

Conclusion:
The DevOps Landscape – Unified, Automated, and Evolving
The DevOps ecosystem has evolved into a sophisticated, interconnected landscape that touches every stage of the software development and delivery lifecycle. From Artifact Management and Source Control to Continuous Integration, Container Orchestration, Security, and AI-powered Analytics, each element plays a critical role in ensuring agility, scalability, security, and speed.
At the heart of DevOps is collaboration and automation — breaking down silos between teams and using powerful tools and practices to streamline operations. Modern organizations are no longer just writing code; they're building resilient, scalable, and secure systems powered by cloud-native principles and intelligent automation.
The future of software delivery hinges on how well businesses can integrate these practices to maximize value streams, enhance user experience, and respond to change faster than ever before. By embracing this comprehensive approach, organizations are not just improving IT—they are transforming themselves into digital-first, innovation-ready enterprises.