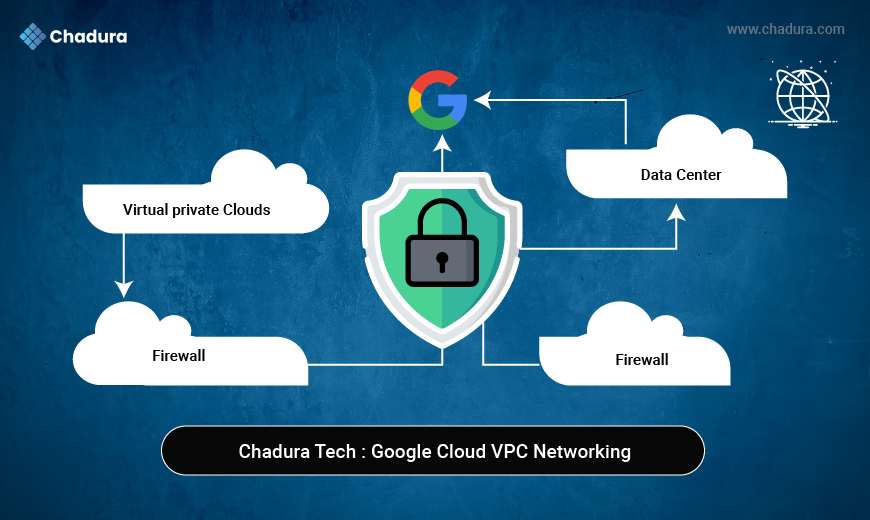
At Chadura Tech, we frequently witness businesses moving to Google Cloud without considering one of the most crucial elements: the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Isolation, secure communication, appropriate traffic control, and smooth integration with on-premises or multi-cloud environments are all guaranteed by a well-designed VPC.
This comprehensive guide explains how to create a VPC in Google Cloud, starting from fundamentals to advanced best practices, with a strong focus on real-world implementation from a Chadura Tech perspective. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced cloud engineer, this guide will help you design and deploy VPCs with confidence.
What Is a VPC in Google Cloud?
In Google Cloud, a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a logically isolated virtual network that offers networking capabilities for your cloud resources, including databases, serverless services, Kubernetes clusters, and Compute Engine virtual machines.
In contrast to conventional data center networks, a GCP VPC is:
- Global (encompasses several regions)
- Extremely scalable
- Software-based
- Completely adaptable
Key Capabilities of Google Cloud VPC
- Define custom IP address ranges
- Create subnets per region
- Control traffic using firewall rules
- Enable private communication between services
- Connect securely to on-premises networks
- Support hybrid and multi-cloud architectures
At Chadura Tech, we treat VPC design as the backbone of cloud architecture, ensuring security, scalability, and long-term flexibility.
Why VPC Is Important in Google Cloud
The Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) in Google Cloud is like a safe, isolated network where you can execute and administer your cloud resources. A VPC supplies the user with absolute control over the flow of data, IP addressing, and connection, at the same time, it is compatible with flexible and trustworthy cloud architectures.
Creating a VPC is often the first step in any GCP project. Here’s why it is critical:
1. Network Isolation
Each VPC is isolated from others by default, ensuring secure separation of environments like development, testing, and production.
2. Security Control
With firewall rules, routing policies, and private IPs, VPCs allow fine-grained traffic control.
3. Scalability
Google Cloud VPCs scale automatically without requiring redesign.
4. Global Reach
A single VPC can span multiple regions, simplifying global application deployments.
5. Hybrid Connectivity
VPCs integrate seamlessly with on-premises networks using VPN or Dedicated Interconnect.
Types of VPC Networks in Google Cloud
1. Default VPC
- Automatically created with a new project
- Includes predefined subnets in each region
- Preconfigured firewall rules
- Suitable for learning and small workloads
2. Auto Mode VPC
- Subnets are automatically created per region
- Uses predefined IP ranges
- Limited customization
- Easy for quick deployments
3. Custom Mode VPC (Recommended by Chadura Tech)
- Full control over subnets and IP ranges
- Better security and scalability
- Ideal for production and enterprise workloads
Chadura Tech strongly recommends Custom Mode VPCs for professional environments.
Key Components of a Google Cloud VPC
Understanding the building blocks of a VPC helps you design better networks.
1. Subnets
- Regional IP address ranges
- Can be expanded without downtime
- Host Compute Engine resources
2. IP Addressing
- Uses CIDR notation (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16)
- Supports private and public IPs
3. Firewall Rules
- Control inbound and outbound traffic
- Stateful by default
- Applied at the network level
4. Routes
- Define how traffic flows
- Automatically created for subnets
- Custom routes supported
5. Peering and Connectivity
- VPC Peering
- Shared VPC
- Cloud VPN
- Cloud Interconnect
Prerequisites to Create a VPC in Google Cloud
Before you begin, ensure the following:
- A Google Cloud account
- An active GCP project
- Billing enabled
- Basic understanding of networking concepts
- IAM permissions (Network Admin or Owner)
Step-by-Step: How to Create a VPC in Google Cloud
Step 1: Log in to Google Cloud Console
Access the Google Cloud Console and select your project.
Step 2: Navigate to VPC Networks
Go to:
Navigation Menu → VPC network → VPC networksStep 3: Click “Create VPC Network”
This opens the VPC configuration page.
Step 4: Configure VPC Details
Network Name
Choose a meaningful name:
chadura-prod-vpcSubnet Creation Mode
Select:
- ✅ Custom
This gives you full control over IP addressing.
Step 5: Create Subnets
Add one or more subnets:
Example Configuration:
- Subnet Name: chadura-app-subnet
- Region: asia-south1
- IP Range: 10.10.0.0/24
You can add multiple subnets across regions as needed.
Step 6: Configure Firewall Rules
Choose whether to:
- Allow SSH
- Allow RDP
- Allow ICMP
At Chadura Tech, we recommend disabling default open rules and creating custom firewall policies later for better security.
Step 7: Enable or Disable Advanced Options
- Enable Private Google Access if required
- Enable VPC Flow Logs for monitoring
- Configure MTU if needed
Step 8: Create the VPC
Click Create. Your VPC network is now ready.
Creating a VPC Using gcloud CLI
For automation and DevOps workflows, CLI is preferred.
Create Custom VPC
gcloud compute networks create chadura-vpc \
--subnet-mode=customCreate a Subnet
gcloud compute networks subnets create chadura-subnet \
--network=chadura-vpc \
--region=asia-south1 \
--range=10.20.0.0/24Creating Firewall Rules for the VPC
Example: Allow SSH
gcloud compute firewall-rules create allow-ssh \
--network=chadura-vpc \
--allow=tcp:22 \
--source-ranges=0.0.0.0/0Best Practices for VPC Design (Chadura Tech Recommendations)
1. Use Custom Mode VPCs
Avoid auto mode for production.
2. Plan IP Addressing Carefully
Design CIDR ranges for future growth.
3. Separate Environments
Use different VPCs for dev, test, and prod.
4. Implement Least Privilege
Restrict firewall rules and IAM permissions.
5. Enable Logging and Monitoring
Use VPC Flow Logs and Cloud Monitoring.
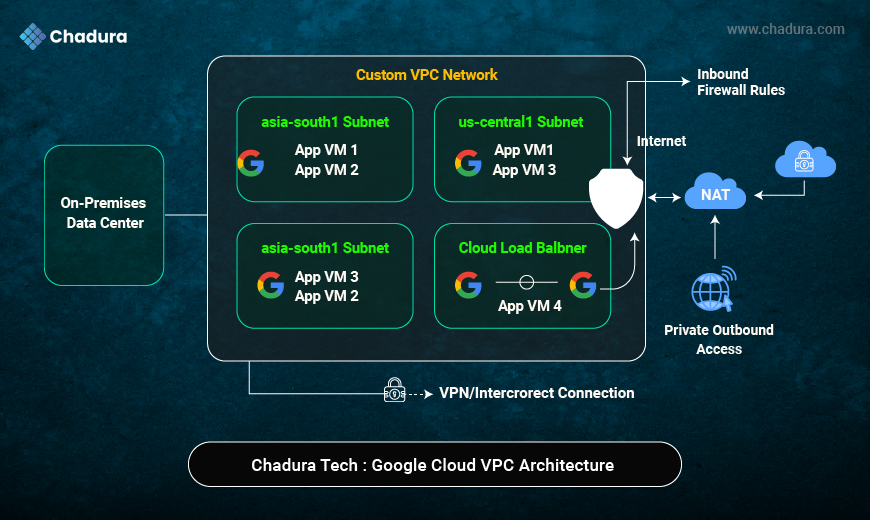
- Google Cloud VPC Architecture : A secure and scalable virtual network that connects cloud resources across regions with full control over IPs, subnets, and traffic flow.
- Custom VPC Network : Provides complete network isolation and customization for enterprise-grade Google Cloud deployments.
- Regional Subnets : Organize workloads by region to improve performance, availability, and latency optimization.
- Compute Engine (App VMs) : Runs application workloads securely inside private subnets without direct internet exposure.
- Cloud Load Balancer : Distributes traffic across multiple VMs to ensure high availability and fault tolerance
- Firewall Rules : Controls inbound and outbound traffic to protect cloud resources from unauthorized access
- Cloud NAT : Enables private VMs to access the internet securely without assigning public IP addresses.
- On-Premises Data Center : Represents existing enterprise infrastructure integrated with Google Cloud.
- VPN / Interconnect : Provides secure, private connectivity between on-premises systems and Google Cloud VPC.
- Use Shared VPC for Enterprises : Centralized networking with multiple projects.
Real-World Use Case: Chadura Tech VPC Design
At Chadura Tech, we design VPCs for:
- SaaS platforms
- FinTech applications
- Healthcare workloads
- AI and data analytics pipelines
Our approach focuses on:
- Security-first architecture
- Cost optimization
- Scalability and automation
Conclusion
Creating a VPC in Google Cloud is more than a technical task—it’s a strategic decision that impacts security, performance, and scalability. A well-planned VPC enables organizations to build reliable cloud infrastructure while maintaining control over networking and costs.
At Chadura Tech, we believe that strong cloud networking is the foundation of digital transformation. By following best practices, choosing custom VPCs, and planning ahead, businesses can unlock the full potential of Google Cloud.
If you’re planning a Google Cloud deployment or need help designing a secure and scalable VPC architecture, Chadura Tech is here to help.