1.What is IAM?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is the foundation of secure digital infrastructure. IAM ensures that the right people and the right workloads have the right access at the right time. It is responsible for:
- User identity validation (authentication)
- Permission and role assignment (authorization)
- Policy enforcement and security compliance
In cloud environments, IAM extends far beyond simple user management. It becomes the central mechanism that protects:
- Applications
- Databases
- Storage
- Compute
- APIs
- Networking
- Serverless functions
IAM determines what a user or a system can do inside your cloud ecosystem.
2. Why IAM Matters for Modern Enterprises
Enterprises across all industries face increasing security challenges:
- Insider threats
- Access misconfigurations
- Unauthorized data exposure
- Complex, distributed workloads
- Compliance mandates
Improper IAM configurations are among the top reasons for cloud breaches.
IAM plays a crucial role in:
2.1 Enforcing Least Privilege
Users and workloads get only what they need—nothing more.
2.2 Enabling Zero-Trust Architecture
Never trust, always verify—every request is validated.
2.3 Improving Operational Efficiency
Centralized access management reduces admin overhead.
2.4 Supporting Compliance
IAM creates enforceable, auditable access paths aligned with global standards:
- ISO/IEC 27001 (International Organization for Standardization)
- SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2)
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
At Chadura Tech, we see IAM as the first line of defense for secure cloud adoption.
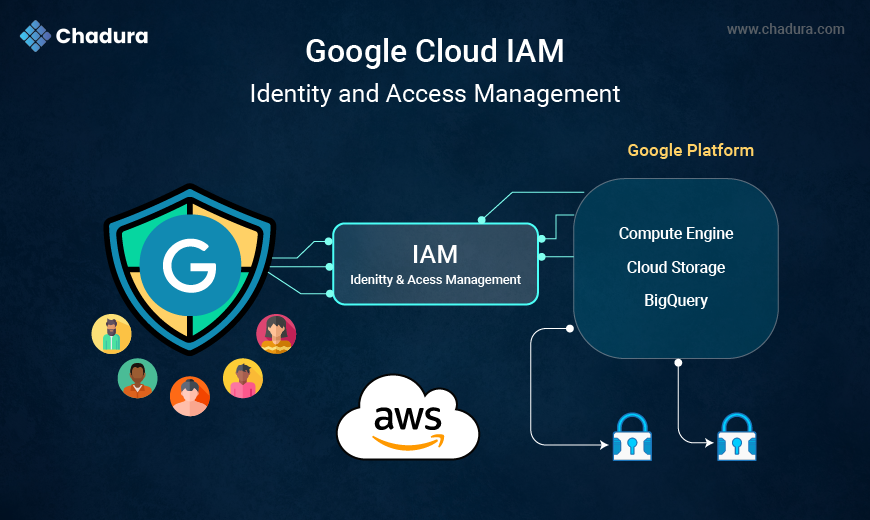
3. Understanding Google Cloud IAM
Understanding Google Cloud IAM provides a clear overview of how Google Cloud manages identities, permissions, and secure access to resources. Learn how IAM roles, policies, and service accounts work together to protect your cloud environment while enabling efficient, role-based access management for users and applications.
Google Cloud IAM is a comprehensive system used to manage access to all Google Cloud services.
It answers three core questions:
- Who can access the resource?
- What can they do?
- How do they gain access?
Google Cloud IAM works across the entire resource hierarchy:
- Organization
- Folders
- Projects
- Services & Sub-resources
From a single place, administrators can manage permissions for:
- Compute Engine
- Cloud Storage
- BigQuery
- Cloud SQL
- Kubernetes Engine
- Cloud Run
- API access
- Networking controls
For enterprises adopting Google Cloud, IAM becomes the backbone of your security model.
4. Core Components of Google Cloud IAM
Core Components of Google Cloud IAM include identities, roles, and policies that work together to control who can access specific resources on Google Cloud. These components form the foundation of secure access management, enabling administrators to assign the right permissions to users, groups, and service accounts across the cloud environment.
Understanding the fundamental IAM components is essential.
4.1 Principals
Entities requesting access:
- Google accounts
- Service accounts
- Cloud Identity users
- Workload identities
- Google groups
4.2 Permissions
Define what action can be performed on a resource.
Example:
storage.objects.list, compute.instances.start, bigquery.tables.update.
4.3 Roles
A set of permissions grouped together.
4.4 Policies
Bindings of:
- Principals
- Roles
- Conditions
IAM policies define the effective access for any resource.
5. IAM Roles Explained
IAM roles determine what level of access someone or something receives.
5.1 Basic Roles (Legacy)
Basic IAM roles—Owner, Editor, and Viewer—provide broad, project-level permissions. They are considered legacy because they grant wide access and are not ideal for enforcing least-privilege security in modern cloud environments.
- Viewer
- Editor
- Owner
NOT recommended in enterprise environments because they are too broad.
5.2 Custom Roles
Custom roles allow administrators to create highly specific permission sets tailored to organizational needs. They help ensure users and services receive only the exact permissions required—nothing more, boosting security and compliance.
For enterprises with specific needs that predefined roles cannot meet.
Chadura Tech often uses custom roles in cases like:
- Granular developer access
- Strict compliance environments
- Restricted audit-only access
- Role separation between operations teams
Custom roles help enterprises avoid privilege overshoot.
6. IAM Policies & Hierarchy
IAM Policies & Hierarchy define how access is granted across Google Cloud’s structured resource model—Organization, Folders, Projects, and Resources. Policies bind identities to roles, and permissions flow downward through the hierarchy, ensuring consistent, scalable, and centrally managed access control.
IAM policies determine who gets what access.
A policy includes:
- Role
- Member
- Condition (optional)
Example:
{
"bindings": [
{
"role": "roles/storage.objectViewer",
"members": ["user:test@chadura.com"]
}
] 6.1 Policy Inheritance
In Google Cloud, policy inheritance means that permissions applied at higher levels—Organization → Folders → Projects → Services—automatically flow down to all lower-level resources. This ensures consistent access control, reduces duplication, and simplifies governance across large GCP environments.This is important for GCP governance:
Org → Folders → Projects → Services
Permissions flow downward.
6.2 IAM Deny Policies
A powerful feature to explicitly block risky actions, e.g.:
- Prevent all users from deleting VMs
- Block external access to sensitive datasets
Chadura Tech recommends using Deny Policies for critical assets.
7. IAM Conditions
IAM Conditions allow context-aware authorization.
Examples:
- Allow access only during working hours
- Allow bucket access only from specific IPs
- Allow VM restart only for DevOps team on weekdays
IAM Conditions enable enterprises to enforce zero-trust access policies with precise control.
8. Identity Federation & Workforce Identity
Identity Federation connects Google Cloud IAM with external identity providers such as:
- Azure AD
- Active Directory
- Okta
- OneLogin
- Ping Identity
This allows you to manage workforce identity from your own identity platform.
8.1 Workforce Identity Federation
Employees can log in without Google accounts.
8.2 Workload Identity Federation
Applications authenticate securely without service account keys.
Enterprises using federation eliminate key management complexity and increase security.
9. Access Controls for Key GCP Services
IAM integrates into every service.
9.1. Compute Engine
Controls:
- Starting/stopping VMs
- Disk access
- Network controls
9.2 Cloud Storage
Controls:
- Bucket-level permissions
- Object-level permissions
- ACLs vs Uniform bucket-level access
9.3 BigQuery
Controls:
- Dataset access
- Table access
- Row-level security
- Column-level access
9.4 Cloud SQL
Controls:
- Instance-level access
- Backup access
- Connection rights
Chadura Tech configures IAM alongside VPC Service Controls for maximum data security.
10. IAM Architecture Blueprint for Enterprises (Recommended by Chadura Tech)
A secure, scalable IAM architecture includes:
1. Organization-Level Security Admins
Protect global policies.
2. Folder-Level Segregation
Separate:
- Production
- Staging
- Development
- Shared resources
3. Project-Level Least Privilege
Assign predefined/custom roles.
4. Identity Federation
Integrate corporate identity systems.
5. Zero-Trust Access Controls
Use IAM Conditions + Context-Aware Access.
6. VPC Service Controls
Protect sensitive data services like BigQuery, Cloud Storage, and Cloud SQL.
7. SCC + Audit Logs
Continuous monitoring.
8. Automated IAM Workflows
Reduce human error.
Chadura Tech establishes this architecture for enterprises moving to GCP.
11. Final Thoughts
Google Cloud IAM is one of the most advanced identity and access governance systems in the cloud ecosystem. With features like:
- Predefined & custom roles
- Hierarchical access structure
- IAM Conditions
- Identity Federation
- Service account security
- Continuous auditing
Enterprises get complete control over “who can do what” across cloud resources.
For organizations migrating to or scaling on Google Cloud, IAM should be the first component of your security and compliance strategy.
At Chadura Tech, we design IAM frameworks that deliver:
- Zero-trust security
- Centralized access governance
- Compliance-ready controls
- Smooth operational workflows
- Scalable identity architecture