Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform developed by Microsoft, offering a wide range of services to build, manage, and deploy applications on a massive, global network. It provides businesses and developers with the tools to innovate, scale, and deliver solutions faster and more efficiently. Launched in 2010, Azure supports multiple programming languages, tools, and frameworks, making it versatile for a broad range of applications. The platform's flexibility, scalability, reliability, and extensive integration capabilities make it a popular choice for organizations looking to leverage cloud technologies.
1. Compute Services
Virtual Machines: Azure's Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) allows users to run virtual servers with full control over the OS and installed applications.
App Services: A Platform as a Service (PaaS) that enables developers to build and host web applications, REST APIs, and backend services.
Azure Functions: This serverless computing option allows users to run code in response to triggers without managing the underlying server infrastructure.
2. Storage Solutions
Azure Blob Storage: A service for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as images, videos, and backups.
Azure File Storage: Managed file shares accessible via REST API or SMB protocol. Great for cloud migration and hybrid applications.
Queue Storage and Table Storage: Solutions designed for large-scale messaging and NoSQL data storage needs.
3. Database Services
Azure SQL Database: A fully managed relational database service offering built-in intelligence and scalability.
Azure Cosmos DB: A globally distributed NoSQL database service designed to scale horizontally and offer low latency.
Azure Database for MySQL/PostgreSQL: Managed database services that provide high availability, scaling, and security.
4. Networking Services
Azure Virtual Network (VNet): Create isolated networks that allow resources to communicate securely.
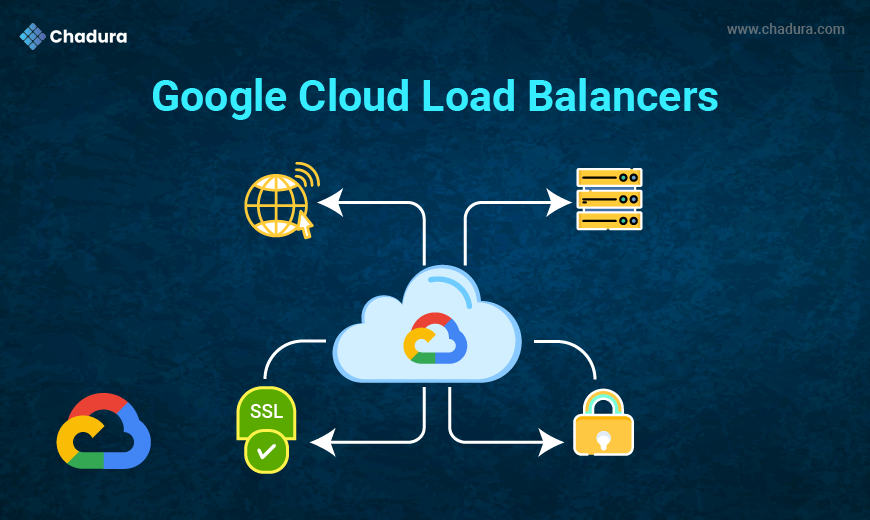
Azure Load Balancer: Automatically distribute incoming traffic across multiple services or VMs to ensure high availability and reliability.
Azure VPN Gateway: Establish secure connections between on-premises networks and Azure networks.
5. AI and Machine Learning
Azure Machine Learning: A suite of tools for building, training, and deploying machine learning models at scale.
Cognitive Services: API suite that provides AI capabilities in areas such as vision (computer vision), speech (speech recognition), and language (natural language processing).
6. IoT Services
Azure IoT Hub: A cloud service for connecting, monitoring, and managing IoT devices at scale.
Azure IoT Central: A fully managed IoT app platform that simplifies and speeds up the development process for connected devices.
7. DevOps Solutions
Azure DevOps: A unified set of tools that support the entire software development lifecycle, including planning, development, testing, and deployment.
Azure Pipelines: Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) services that can work with any language, platform, and cloud.
8. Security and Identity
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD): An identity and access management service that helps users manage and secure identities and access to applications.
Azure Firewall and DDoS Protection: Security services to protect Azure applications and networks from threats.
9. Content Delivery Network
Azure CDN: A global content delivery network that ensures fast content delivery through cache servers distributed worldwide to reduce latency.
10. Management and Monitoring
Azure Monitor: Tool for collecting, analyzing, and acting on telemetry data from Azure and on-premises environments.
Azure Automation: Automates cloud management processes, allowing users to orchestrate tasks across Azure and other environments.
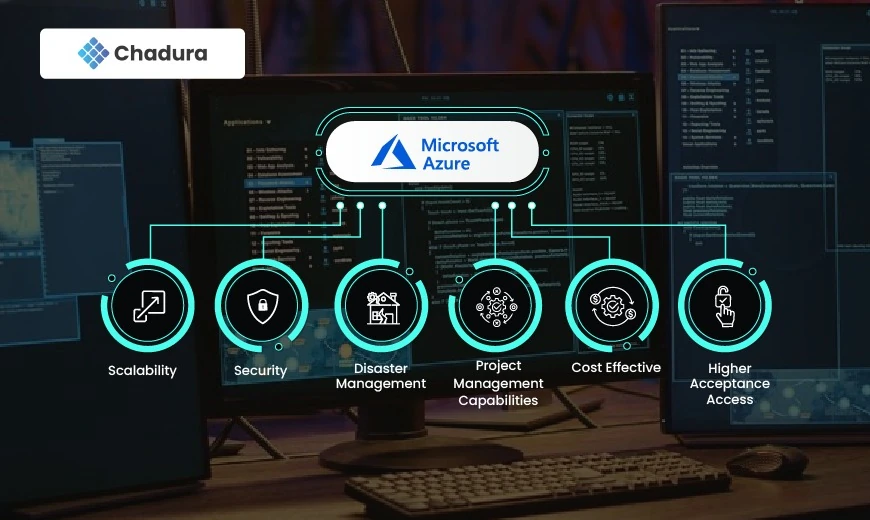
Benefits of Azure
Scalability: Resources can be scaled up or down based on demand.
Global Reach: Azure has data centers across various geographic regions, allowing for localization and redundancy.
Hybrid Compatibility: Offers hybrid capabilities that allow integration with on-premises data and other clouds.
Robust Security: Adheres to numerous compliance standards and offers advanced security features.
Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing models help manage costs efficiently.
Popular Use Cases:
- Hosting websites and web apps
- AI and machine learning solutions
- Big data analytics
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications
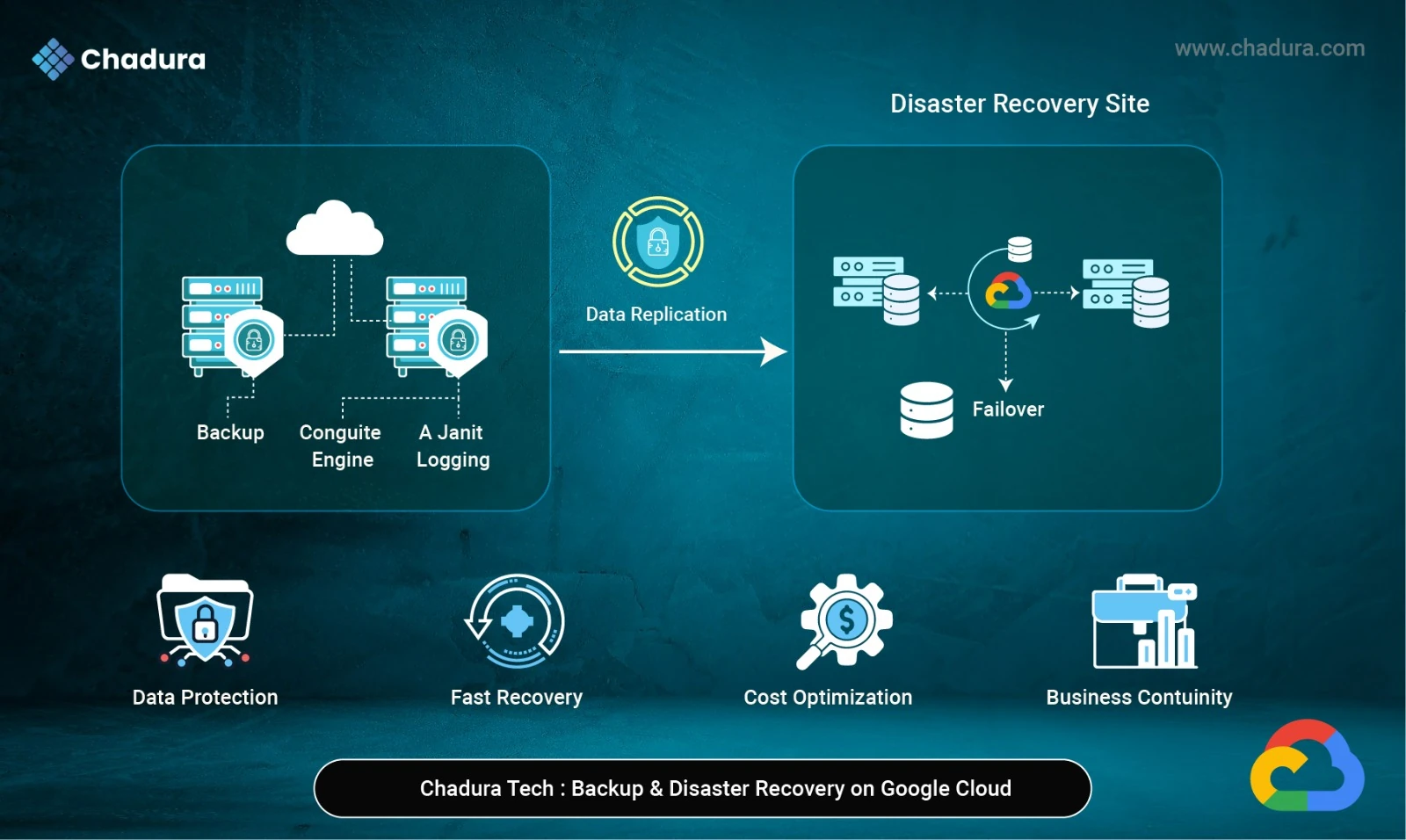
- Disaster recovery and backup solutions
- Video game development and hosting