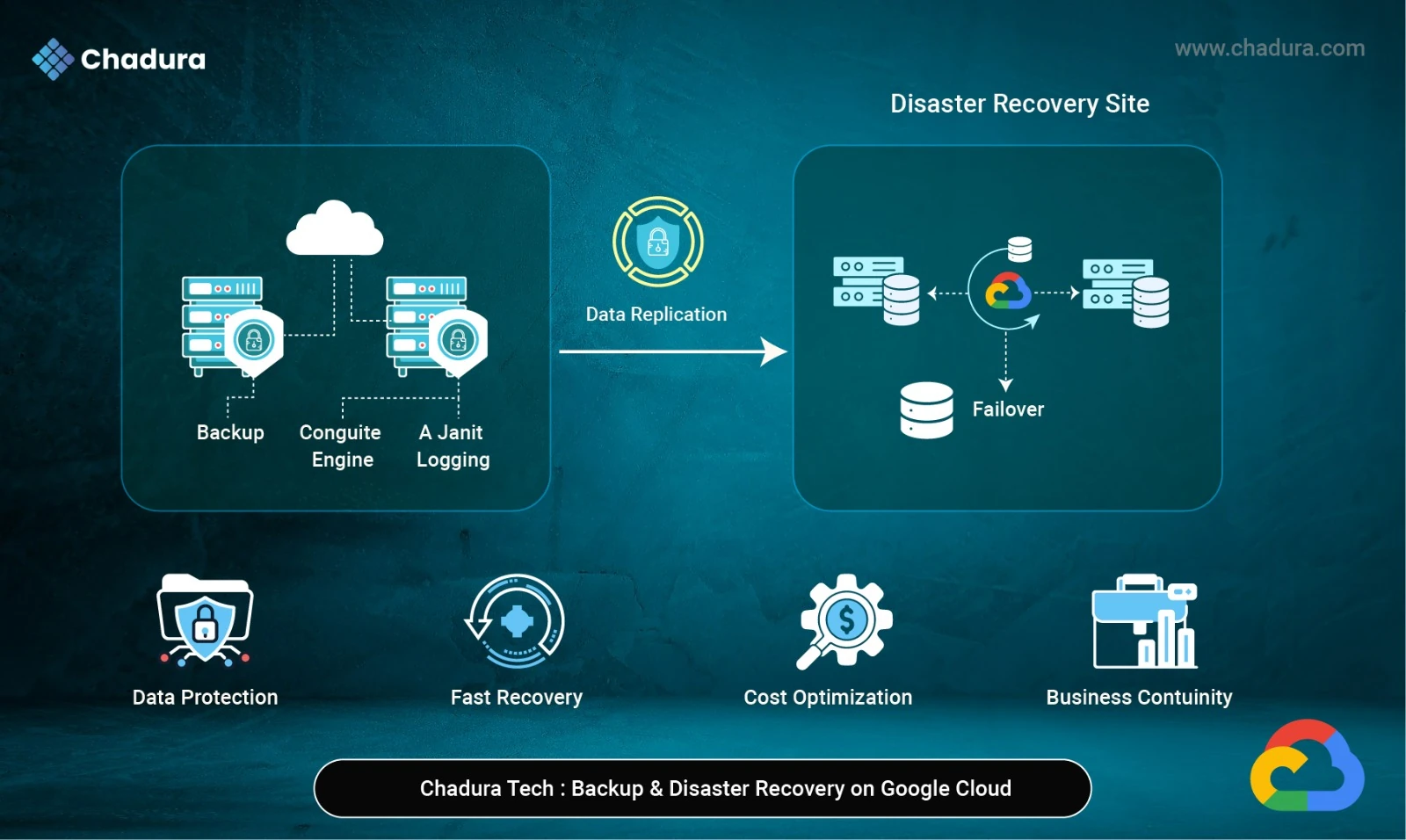
What Is Backup and Disaster Recovery?
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) is the process of protecting data and systems so they can be quickly restored in case of failures, data loss, cyberattacks, or disasters. Backup creates copies of data for recovery, while Disaster Recovery ensures applications and services continue running or are rapidly restored during major outages, ensuring business continuity.
Backup
Backup refers to creating copies of data so it can be restored in case of:
- Accidental deletion
- Data corruption
- Ransomware attacks
- Application failure
Backups are typically used for data recovery, not full infrastructure recovery.
Disaster Recovery (DR)
Disaster Recovery focuses on restoring entire systems and services after major failures such as:
- Data center outages
- Regional failures
- Large-scale cyber incidents
- Natural disasters
DR includes:
- Infrastructure recovery
- Application availability
- Network and security restoration
Why Backup and Disaster Recovery Are Critical on Google Cloud
Backup and Disaster Recovery are critical on Google Cloud because Google secures the infrastructure, but customers are responsible for protecting their data and applications. Without proper backups and a disaster recovery plan, accidental deletions, outages, or cyber incidents can still cause data loss and downtime, impacting business continuity.
Many organizations assume that moving to the cloud automatically makes their data safe. This is a dangerous misconception.
Google Cloud Shared Responsibility Model
Google Cloud secures:
- Physical data centers
- Network infrastructure
- Hardware reliability
Customers are responsible for:
- Application-level data
- Backups
- Disaster recovery planning
- Security configurations
Without a proper BDR strategy, even cloud-hosted workloads are at risk.
Key Business Benefits of a Strong BDR Strategy
A strong Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) strategy minimizes downtime, prevents data loss, and ensures fast recovery during failures. It also improves business continuity, regulatory compliance, and customer trust.
From Chadura Tech’s experience, organizations that implement structured backup and DR on Google Cloud gain:
- Minimal downtime
- Fast data recovery
- Regulatory compliance
- Business continuity assurance
- Lower financial risk
- Customer trust
Understanding RPO and RTO (Core DR Metrics)
Before choosing tools, it’s important to define two key metrics:
RPO (Recovery Point Objective) defines how much data loss a business can tolerate, measured in time.
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) defines how quickly systems and services must be restored after an outage.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- How much data loss is acceptable?
- Example: RPO of 15 minutes means you can lose up to 15 minutes of data.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
- How quickly systems must be restored?
- Example: RTO of 1 hour means services must be back online within one hour.
Chadura Tech always recommends defining RPO and RTO before designing backup and DR architecture.
Google Cloud Backup Solutions (Data-Level Protection)
Google Cloud Backup Solutions provide data-level protection using tools like snapshots, managed backups, and database-native backup features. These solutions help safeguard data against accidental deletion, corruption, and failures while enabling quick and reliable restoration.
1. Google Cloud Backup and DR (Backup and DR Service)
Google Cloud offers a managed Backup and DR service designed for enterprise workloads.
Key features:
- Centralized backup management
- Application-consistent backups
- Support for Compute Engine, databases, and file systems
- Automated backup policies
- On-demand and scheduled backups
Best use cases:
- Enterprise VM workloads
- Compliance-driven environments
- Organizations needing centralized control
2. Compute Engine Snapshots
Snapshots are one of the most commonly used backup methods in Google Cloud.
How it works:
- Creates incremental backups of persistent disks
- Stored in Cloud Storage
- Can be restored to new or existing VMs
Advantages:
- Fast and simple
- Incremental (cost-efficient)
- Easy automation using schedules
Limitations:
- Not application-aware by default
- Not ideal for complex database consistency without additional steps
Chadura Tech Recommendation:
Use snapshots for VM-level backups, combined with database-level backups for critical workloads.
3. Cloud Storage Backup Options
Google Cloud Storage provides built-in durability and versioning features.
Object Versioning
- Keeps older versions of objects
- Protects against accidental overwrites or deletions
Bucket Lock (Retention Policies)
- Enforces data retention for compliance
- Prevents deletion before retention period ends
Best for:
- Logs
- Media files
- Static data
- Backup archives
4. Database-Specific Backup Solutions
Cloud SQL Backups
- Automated daily backups
- Point-in-time recovery
- Manual backup triggers
Cloud Spanner Backups
- Managed backups with minimal performance impact
- Cross-region restore capability
BigQuery Data Protection
- Table snapshots
- Time travel (up to 7 days)
Chadura Tech Insight:
Always use native database backup features in addition to infrastructure backups.
Disaster Recovery Solutions in Google Cloud
Backup alone is not enough. Disaster recovery focuses on service availability.
1. Multi-Zone and Multi-Region Architecture
Google Cloud regions consist of multiple zones. A zone failure should not bring down applications.
Best practices:
- Deploy workloads across multiple zones
- Use managed instance groups
- Load balance traffic across zones
2. Google Cloud Load Balancing
Google’s global load balancers help route traffic to healthy backends.
Benefits for DR:
- Automatic failover
- Global IP addresses
- Health checks
If one region fails, traffic can be redirected to another region.
3. Active-Passive DR Architecture
In this setup:
- Primary region handles live traffic
- Secondary region remains on standby
- Data is replicated continuously
Pros:
- Lower cost than active-active
- Easier to manage
Cons:
- Some downtime during failover
Chadura Tech Use Case:
Ideal for medium-sized enterprises with moderate RTO requirements.
4. Active-Active DR Architecture
Both regions serve live traffic simultaneously.
Pros:
- Near-zero downtime
- High availability
Cons:
- Higher cost
- Complex data synchronization
Best for:
- Financial services
- E-commerce
- Mission-critical applications
5. Database Replication for DR
Google Cloud supports:
- Read replicas (Cloud SQL)
- Cross-region replication
- Multi-region Spanner instances
This ensures data availability even if a region becomes unavailable.
Cost Optimization for Backup and DR
Cost optimization for Backup and Disaster Recovery involves using incremental backups, applying storage lifecycle policies, and selecting the right storage classes like Nearline or Coldline. This helps reduce costs while maintaining reliable data protection and recovery readiness.
Backup and DR can become expensive if not planned carefully.
Cost Optimization Tips:
- Use incremental backups
- Apply lifecycle rules
- Store long-term backups in Nearline or Coldline
- Delete unused snapshots
- Right-size DR environments
Chadura Tech Tip:
Balance cost with business risk, not just storage price.
Common Backup and DR Mistakes We See
From real client engagements, Chadura Tech frequently encounters:
- No documented DR plan
- Untested backups
- Single-region deployments
- Over-retention of backups
- Lack of access control
- Assuming Google Cloud handles everything
Avoiding these mistakes can save organizations from major outages.
Chadura Tech’s Recommended Backup and DR Strategy
Our proven approach includes:
- Define RPO and RTO
- Classify workloads by criticality
- Use native Google Cloud backup tools
- Implement multi-zone or multi-region architecture
- Automate backup and DR processes
- Secure backup data
- Regularly test and improve the DR plan
Final Thoughts
Backup and Disaster Recovery are not optional—they are essential components of any cloud strategy. Google Cloud provides powerful, scalable, and reliable tools for protecting data and ensuring business continuity. However, the effectiveness of these tools depends entirely on how well they are designed, implemented, and tested.
At Chadura Tech, we believe in building simple, practical, and cost-effective backup and disaster recovery solutions tailored to real business needs. Whether you are running a single application or managing enterprise-scale workloads, a well-planned BDR strategy on Google Cloud can protect your business from unexpected disruptions.